codecarbon
Track emissions from Compute and recommend ways to reduce their impact on the environment.
Estimate and track carbon emissions from your computer, quantify and analyze their impact.
About CodeCarbon 💡
CodeCarbon started with a quite simple question:
What is the carbon emission impact of my computer program? :shrug:
We found some global data like "computing currently represents roughly 0.5% of the world’s energy consumption" but nothing on our individual/organisation level impact.
At CodeCarbon, we believe, along with Niels Bohr, that "Nothing exists until it is measured". So we found a way to estimate how much CO2 we produce while running our code.
How?
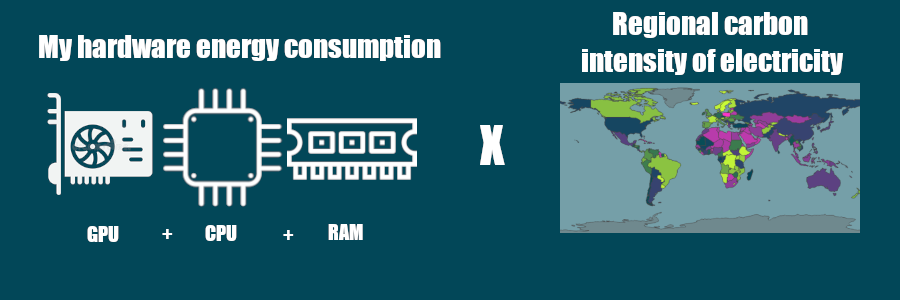
We created a Python package that estimates your hardware electricity power consumption (GPU + CPU + RAM) and we apply to it the carbon intensity of the region where the computing is done.
We explain more about this calculation in the Methodology section of the documentation.
Our hope is that this package will be used widely for estimating the carbon footprint of computing, and for establishing best practices with regards to the disclosure and reduction of this footprint.
So ready to "change the world one run at a time"? Let's start with a very quick set up.
Quickstart 🚀
Installation 🔧
From PyPI repository
pip install codecarbon
From Conda repository
conda install -c codecarbon codecarbon
To see more installation options please refer to the documentation: Installation
Start to estimate your impact 📏
To get an experiment_id enter:
! codecarbon init
You can now store it in a .codecarbon.config at the root of your project
[codecarbon] log_level = DEBUG save_to_api = True experiment_id = 2bcbcbb8-850d-4692-af0d-76f6f36d79b2 #the experiment_id you get with init
Now you have 2 main options:
Monitoring your machine 💻
In your command prompt use:
codecarbon monitor
The package will track your emissions independently from your code.
In your Python code 🐍
from codecarbon import track_emissions @track_emissions() def your_function_to_track(): # your code
The package will track the emissions generated by the execution of your function.
There is other ways to use codecarbon package, please refer to the documentation to learn more about it: Usage
Visualize 📊
You can now visualize your experiment emissions on the dashboard.
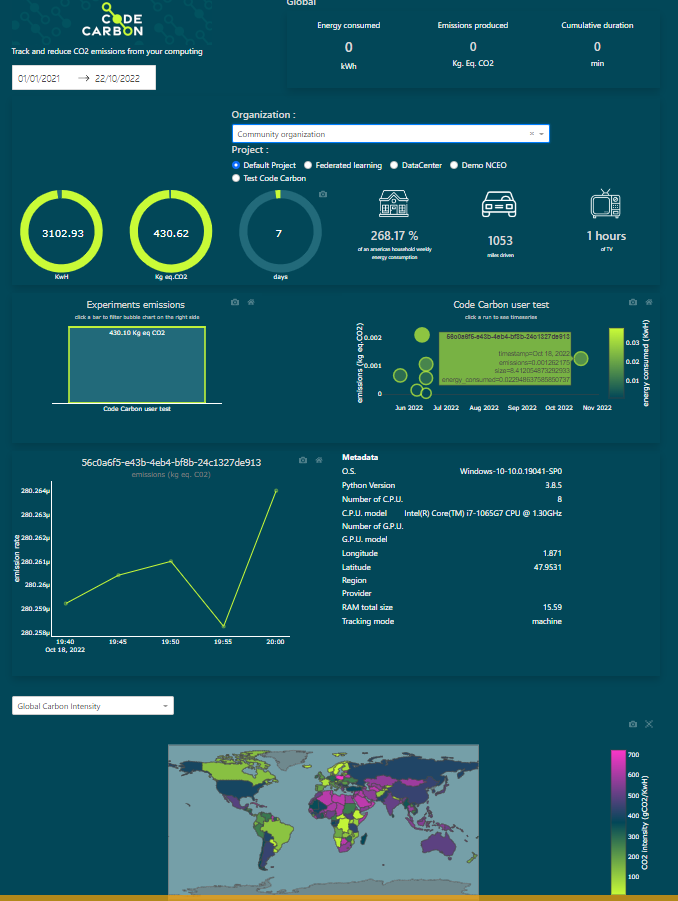
Note that for now, all emissions data send to codecarbon API are public.
Hope you enjoy your first steps monitoring your carbon computing impact! Thanks to the incredible codecarbon community 💪🏼 a lot more options are available using codecarbon including:
- offline mode
- cloud mode
- comet integration...
Please explore the Documentation to learn about it If ever what your are looking for is not yet implemented, let us know through the issues and even better become one of our 🦸🏼♀️🦸🏼♂️ contributors! more info 👇🏼
Contributing 🤝
We are hoping that the open-source community will help us edit the code and make it better!
You are welcome to open issues, even suggest solutions and better still contribute the fix/improvement! We can guide you if you're not sure where to start but want to help us out 🥇
In order to contribute a change to our code base, please submit a pull request (PR) via GitHub and someone from our team will go over it and accept it.
Check out our contribution guidelines :arrow_upper_right:
Contact @vict0rsch to be added to our slack workspace if you want to contribute regularly!
How To Cite 📝
If you find CodeCarbon useful for your research, you can find a citation under a variety of formats on Zenodo.
Here is a sample for BibTeX:
@software{benoit_courty_2024_11171501, author = {Benoit Courty and Victor Schmidt and Sasha Luccioni and Goyal-Kamal and MarionCoutarel and Boris Feld and Jérémy Lecourt and LiamConnell and Amine Saboni and Inimaz and supatomic and Mathilde Léval and Luis Blanche and Alexis Cruveiller and ouminasara and Franklin Zhao and Aditya Joshi and Alexis Bogroff and Hugues de Lavoreille and Niko Laskaris and Edoardo Abati and Douglas Blank and Ziyao Wang and Armin Catovic and Marc Alencon and Michał Stęchły and Christian Bauer and Lucas Otávio N. de Araújo and JPW and MinervaBooks}, title = {mlco2/codecarbon: v2.4.1}, month = may, year = 2024, publisher = {Zenodo}, version = {v2.4.1}, doi = {10.5281/zenodo.11171501}, url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11171501} }
Contact 📝
Maintainers are @vict0rsch @benoit-cty and @SaboniAmine. Codecarbon is developed by volunteers from Mila and the DataForGoodFR community alongside donated professional time of engineers at Comet.ml and BCG GAMMA.
Star History
Comparison of the number of stars accumulated by the different Python CO2 emissions projects:
Previous
Zürich Green IT Hackathon
Next project